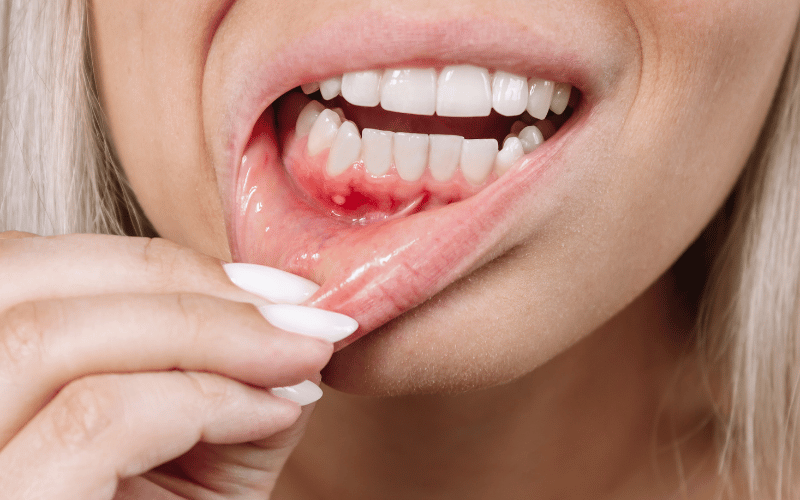
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, affects millions worldwide, varying prevalence rates by region and demographics. However, what may surprise many is the intricate link between oral health and heart health. Recent research suggests that untreated gum disease can significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular issues, such as heart attacks and strokes.
This raises a critical question: Did you know that neglecting your gum health could potentially impact the health of your heart? Understanding this connection underscores the importance of comprehensive oral care for overall well-being.
The Connection Between Gum Disease and Heart Health
Periodontal disease and heart health are intertwined through inflammation and bacterial spread. Periodontal disease triggers inflammation in the gums, which, if left untreated, can spread bacteria into the bloodstream. These oral bacteria can then travel to the heart, exacerbating atherosclerosis by promoting plaque buildup in arteries.
Additionally, they can infect heart valves, leading to severe complications. This journey highlights the intricate connection between oral health and cardiovascular well-being, emphasizing the need for proactive dental care to safeguard overall heart health.
Risk Factors for Both Periodontal Disease and Heart Disease
Several risk factors contribute to both periodontal disease and heart disease. These include:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing, flossing, and dental care can lead to plaque buildup on teeth, increasing the risk of gum disease and potentially contributing to heart problems.
2. Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for both gum disease and heart disease, as it constricts blood vessels, reduces oxygen flow, and weakens the immune system.
3. Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more prone to gum disease, and poorly controlled diabetes can exacerbate both gum and heart conditions.
4. Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing both periodontal disease and heart disease due to inflammation and other metabolic factors.
5. Poor Diet: Consuming a diet high in sugars, processed foods, and saturated fats can contribute to gum inflammation, plaque buildup, and heart disease risk.
6. Stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and increase inflammation, potentially worsening gum and heart health.
Addressing these shared risk factors through lifestyle modifications and regular dental check-ups can help mitigate the risk of periodontal disease and heart disease.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease and Warning Signs for Heart Issues
Periodontal disease (gum disease) symptoms and warning signs for heart issues may overlap, underscoring their interconnectedness.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
1. Swollen, Red Gums: Inflammation and irritation are common in the early stages of gum disease.
2. Bleeding Gums: Gums may bleed during brushing, flossing, or even spontaneously.
3. Persistent Bad Breath: Bacteria buildup in the mouth can cause chronic bad breath (halitosis).
4. Receding Gums: Gums may pull away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth’s root.
5. Loose or Shifting Teeth: As gum disease progresses, teeth may become loose or shift position.
6. Painful Chewing: Discomfort or pain while chewing can indicate advanced gum disease, which affects the teeth and gums’ supporting structures.
Warning Signs for Heart Issues
1. Chest Pain or Discomfort: This may feel like pressure, tightness, or squeezing in the chest, which could indicate angina or a heart attack.
2. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath can occur with heart failure or a heart attack.
3. Fatigue: Unexplained fatigue or weakness, especially if severe or lasts several days, could indicate heart trouble.
4. Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Feeling faint, dizzy, or lightheaded may indicate a heart arrhythmia or other cardiovascular issue.
5. Swelling: Swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or abdomen can indicate heart failure or other heart-related problems.
While some symptoms may be specific to either periodontal disease or heart issues, individuals experiencing any of these symptoms should seek medical or dental attention promptly to address potential underlying health concerns. Regular dental check-ups and heart health assessments can help catch issues early and prevent complications.
Prevention and Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease
Prevention and treatment of periodontal disease involve a combination of good oral hygiene practices, lifestyle modifications, and professional dental care. Here are some key strategies:
Prevention:
1. Regular Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent buildup.
2. Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while limiting sugary snacks and beverages.
3. Avoid Tobacco: Quit smoking or using tobacco products, as they significantly increase the risk of gum disease.
4. Regular Dental Visits: Visit your dentist for routine check-ups and professional cleanings every six months or as recommended.
5. Manage Stress: Stress can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to gum disease. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as exercise, meditation, or yoga.
Treatment:
1. Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning removes plaque and tartar below the gumline and smooths the tooth roots to promote healing.
2. Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infection and reduce inflammation.
3. Surgical Procedures: Advanced cases of periodontal disease may require surgical interventions such as flap surgery, bone grafts, or tissue regeneration procedures to restore gum and bone health.
4. Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthier lifestyle, including regular exercise, stress management, and a balanced diet, can support gum tissue healing and oral health.
5. Maintenance: After treatment, it’s crucial to maintain good oral hygiene habits and attend regular dental check-ups to prevent the recurrence of gum disease.
Steps to Take to Protect Your Heart Health
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit intake of processed foods, saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
2. Stay Active: Engage in regular physical activity most days of the week. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, as well as muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Strive to achieve and maintain a healthy weight by balancing calorie intake with physical activity. Avoid crash diets and excessive weight loss procedures.
4. Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quit immediately. Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions. Seek help from healthcare specialists or smoking cessation programs if necessary.
5. Limit Alcohol Consumption: If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Limit your alcohol consumption to one drink per day for ladies and two for males.
Wrap Up!
Prioritizing oral and heart health is paramount in pursuing a healthier life. By recognizing the intricate connection between periodontal disease and heart issues, we empower ourselves to take proactive steps. Remember, regular dental check-ups, a nutritious diet, and exercise protect our smiles and safeguard our hearts.
For more information on periodontal disease and heart health, consult reputable sources like dental or cardiologist associations. For top-notch periodontal maintenance in Burbank, trust DNA Dental Studio Burbank. Take charge of your health today – schedule your appointment and smile confidently towards a healthier tomorrow!